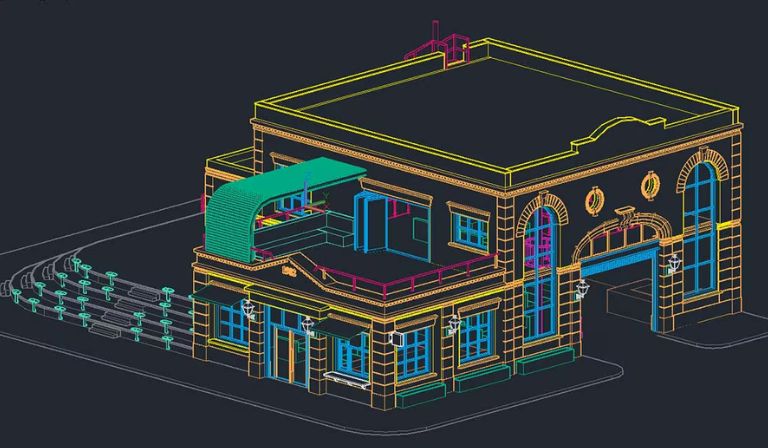
AutoCAD, short for Automatic Computer-Aided Design, is a versatile software that has revolutionized industries such as architecture, engineering, and interior design. With its powerful tools and features, it enables users to create intricate 2D and 3D designs with precision. However, tackling AutoCAD assignments can be daunting, especially for beginners. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive roadmap to mastering AutoCAD assignments, helping you navigate through challenges and develop proficiency.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding AutoCAD Basics
Before delving into assignments, it is essential to grasp the fundamentals of AutoCAD. The software’s interface might seem overwhelming at first, but breaking it down into sections simplifies the learning process. Key components include:
- Command Line: The heart of AutoCAD, where you can type commands directly.
- Ribbon: A dynamic toolbar providing access to drawing, modifying, and annotating tools.
- Model Space and Layouts: The workspace where designs are created and prepared for presentation or printing.
- Coordinate System: Understanding the Cartesian coordinate system is crucial for precision in drawing.
Familiarity with these components forms a strong foundation, making it easier to approach complex tasks.
Setting Up for Success
AutoCAD assignments often require meticulous planning and setup to ensure accuracy and efficiency. Here are some preparatory steps:
- Understand the Assignment Brief: Read the instructions carefully to identify the goals and deliverables. Highlight key requirements such as dimensions, file formats, or specific tools to be used.
- Gather Reference Materials: Ensure you have access to all necessary data, including blueprints, sketches, or images, which will guide your drawing.
- Template Selection: Choose an appropriate template to match the assignment’s requirements. AutoCAD provides a variety of default templates, or you can create a custom one.
- Units and Scale: Set the correct units (e.g., metric or imperial) and define the drawing scale. This step ensures consistency and accuracy.
- Layer Organization: Use layers to segregate different elements of your drawing, such as walls, text, and dimensions. Assign distinct colors and line types to maintain clarity.
Key Tools and Techniques
AutoCAD boasts a plethora of tools, and mastering the most commonly used ones will streamline your workflow. Below are some essential tools and techniques to focus on:
- Drawing Tools:
- Line: For creating straight lines.
- Circle and Arc: For round and curved shapes.
- Rectangle and Polygon: For geometric figures.
- Polyline: Combines multiple line and arc segments into a single entity.
- Modify Tools:
- Move and Copy: To reposition and duplicate objects.
- Trim and Extend: To adjust object lengths.
- Rotate and Mirror: For altering orientation and creating symmetrical designs.
- Offset: To create parallel lines or shapes.
- Annotation Tools:
- Text: Add labels or notes to your drawing.
- Dimensions: Display measurements to provide clarity.
- Hatch: Fill areas with patterns or solid colors for emphasis.
- Snapping and Grids: Use object snaps (OSNAP) and grid settings to ensure precision in alignment and placement.
Tackling 2D Drawings
Most introductory AutoCAD assignments focus on 2D drawings. To excel, follow these steps:
- Start Simple: Begin with basic shapes and gradually add details. For example, when designing a floor plan, outline the walls first before adding doors, windows, and furniture.
- Use Layers Effectively: Assign layers for different elements (e.g., electrical, plumbing) and toggle visibility as needed to avoid clutter.
- Leverage Blocks: Create reusable components like doors or chairs as blocks. This practice saves time and ensures uniformity.
- Dimensioning: Add dimensions to indicate sizes and distances. Ensure they are legible and conform to assignment standards.
Exploring 3D Modeling
Advanced assignments may involve 3D modeling, a feature that adds depth and realism to designs. While it is more complex, the results are rewarding. To approach 3D tasks:
- Switch to 3D Workspace: Adjust the interface to access 3D tools such as Extrude, Revolve, and Sweep.
- Start with 2D: Draw a 2D profile and use tools like Extrude or Revolve to convert it into a 3D object.
- Modify in 3D: Use tools like Fillet and Chamfer to refine edges and add realism.
- Visual Styles: Experiment with visual styles (e.g., Wireframe, Realistic) to assess your model’s appearance.
- Render for Impact: Apply materials and lighting to create realistic renderings that enhance your presentation.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
AutoCAD assignments often come with challenges. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
- Misaligned Objects: Use OSNAP and grid settings to ensure precise alignment.
- Unclear Dimensions: Double-check scales and units. Use the Dimension tool to clarify.
- Cluttered Drawings: Organize elements using layers and freeze unnecessary layers temporarily.
- File Corruption: Save versions regularly and maintain backups to prevent data loss.
- Slow Performance: Optimize by purging unused elements and avoiding overly detailed blocks.
Enhancing Efficiency
Efficiency is crucial in meeting deadlines without compromising quality. Here are some tips:
- Keyboard Shortcuts: Learn shortcuts for frequently used commands to speed up workflow.
- Dynamic Input: Enable dynamic input to display commands and dimensions near the cursor.
- Tool Palettes: Customize tool palettes for quick access to favorite tools and blocks.
- Customization: Tailor the interface to suit your preferences by rearranging toolbars and menus.
- External References (Xrefs): Use Xrefs to link external files instead of copying them into your drawing, keeping files lightweight.
Learning Resources
To further enhance your AutoCAD skills, utilize a variety of resources:
- Online Tutorials: Many platforms offer step-by-step tutorials for all proficiency levels.
- User Manuals: AutoCAD’s official documentation provides in-depth insights.
- Forums and Communities: Engage with online forums to seek advice and share knowledge.
- Practice Assignments: Regular practice helps reinforce concepts and improve proficiency.
- Workshops and Courses: Attend workshops or enroll in courses for structured learning.
Final Tips for Assignment Success
- Allocate Time Wisely: Break down the assignment into manageable tasks and set milestones.
- Review Before Submission: Double-check every element for accuracy and completeness.
- Seek Feedback: Share your work with peers or mentors for constructive criticism.
- Stay Updated: Familiarize yourself with the latest AutoCAD features to stay ahead.
Conclusion
AutoCAD is a powerful tool that requires patience and practice to master. By understanding its features, organizing your workflow, and leveraging available resources, you can tackle assignments with confidence. Whether you’re designing a simple 2D layout or an intricate 3D model, the key to success lies in attention to detail and continuous learning. With consistent effort, you can transform your AutoCAD assignments into works of precision and creativity, paving the way for a promising future in design and engineering.